Develop the
Client-Side-Class for the Business Object 'Project' -
Fat-Client-Development
Business
Objects are entities that keep together data belonging to one
'business-area'; e.g. an invoice with a 'header' and several
'positions'.
Business Objects can contain data that is physically
stored on different database-tables.
For
the theory about Business Objects please consult Using
Business Objects to handle data-storage and retrieval.
The
Client-Side Class inherits from the General Class and implements
methods which are needed on the client side of an application.
Furthermore,
this document deals how the Client-Side Buseiness Object is defined
as a variable in a Task-Frame and what methods have to be called when
the user clicks the 'Store' button.
Preface:
If
you are came to this document to get a guideline for developing a
Business Object, I recommend to start with the document Business
Object, Overview – Advanced Java Fat-Client-Development
or go directly to the ToDo-List in document Business
Object, Client-Sidel Class – Advanced Java
Fat-Client-Development.
As
classes for Business Objects have a critical mission within an
application, preference was given to performance if there has to be
made a decision between understandability and performance.
I hope,
that the comments placed in the code will help you to understand what
intention is behind the code.
Credits:
Too
numerous to mention; the idea is available in dozens of versions –
I refined a lot of ideas into my system.
Prerequisites:
Create
the Client-Side Business Object for 'Project':
As
lined out in Using
Business Objects to handle data-storage and retrieval, a Business
Object will be derived into a Server-Side- and a Client-Side-Version.
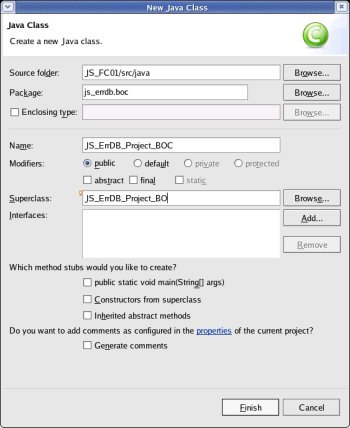
To
create the class for the Client-Side, right click onto the project
'JS_FC01' and select >New>Class
Enter
the Package (js_errdb.boc),
the (Class-)Name (JS_ErrDB_Project_BOC
– note
the 'C' at the end, please),
enter or 'Browse' the Superclass (JS_ErrDB_Project_BO)
and check that no checkbox is selected; then click the [Finish]
button.
Eclipse
has already generated a template and the individual code can be
entered.
Please see the code to be entered at
JS_ErrDB_Project_BOC
- or copy it from there ;-) .
A
list with the major steps to do follows.
top.
Code
the variable for the (calling) Task-Frame and the constructor:
In
the Task-Frame there have to be two objects of the Client-Side
derivation of a Business Object:
* One that helds the values at
the time when the Business Object was read and
* One that helds
the values that reflect the changes of the user made at entry
fields.
This allows to enable/disable buttons depending if
changes were made that might be stored.
/*
* Business
Objects maintained within this task. */
protected
JS_ErrDB_Project_BOC structJS_ErrDB_Project_BOC_Read;
protected
JS_ErrDB_Project_BOC structJS_ErrDB_Project_BOC_Processed;
The
construction of the Business Objects is done in method
initialize_before_frame:
private
void initialize_before_frame(String
parmstrLanguageCode) {
/*
Construct the Business Objects maintained by this task.
*/
structJS_ErrDB_Project_BOC_Read
= new
JS_ErrDB_Project_BOC(this);
structJS_ErrDB_Project_BOC_Processed
= new
JS_ErrDB_Project_BOC(this);
top.
Code
the method to transfer values from GUI-elements to the variables of
this Business Object:
As
the text entered by the user has to be brought to the variables of
the Business Object, a method is developed that extract the values
of GUI-elements.
First
there are some basic methods requiered.
If you downloaded the
JAR-file with the base-classes (see JS_FC01cb
– Download the jar-file for the base-classes), then you
can call the methods without further coding.
If you are coding
the base-classes step by step (then you started with JS_FC01ca
– Create a project for the base-classes), I recommend to
print out the class JSBS_FrameServices
and code the methods as requiered.
With
using the methods JSBS_FrameServices,
the transfer of variables is pretty simple.
Please obey, that
there is always an if condition, if there was a parameter
passed.
This is a provision, if a variable of a Business Object
has no counterpart on the GUI and the value has to be set to a
default value or has to be computed depending on other values.
/*
*
Method to take the values from the GUI (Graphic-User-Interface)
Elements
* and transfer it to the variables of the
Business Object. */
public
void getFromGUI(JTextField
parmProjectCode,
JTextField
parmLanguageCode,
JTextField
parmTargetDirectory) {
if
(parmProjectCode != null)
{
ProjectCode
= JSBS_FrameServices.getTextFromJTextField(parmProjectCode);
}
if
(parmLanguageCode
!= null)
{
LanguageCode
= JSBS_FrameServices.getTextFromJTextField(parmLanguageCode);
}
if
(parmTargetDirectory
!= null)
{
TargetDirectory
= JSBS_FrameServices.getTextFromJTextField(parmTargetDirectory);
}
}
top.
Code
the method to 'store' the Business Object on the database:
As
the main code to perform database-operations is in the Server-Side
derivation of a Business Object, the main function of the method on
the Client-Side is to decide, if the application is configured as
'Stand-Alone' (i.e. the database-system runs on the same machine as
the user works) or as 'Fat-Client' (i.e. the database-system runs on
an extra machine with as Java Application Server installed and
access to the data is made using the EJB technology).
To
be noticed:
As
the class JS_ErrDB_Project_BOS
is not already coded, copying the method from
JS_ErrDB_Project_BOC
will lead to a compilation error.
To
avoid this error, all lines referring to not yet implemented classes
(i.e. Server-Side derivation of the Business Object and the class
that communicates over EJB with a JAS), should be commented
out.
This allows to use the debugger in a later step.
If
you code step by step (and do not copy from JS_ErrDB_Project_BOC),
just implement the following code:
/*
* --------------------
*
Method to store the new entered or changed values of this Business
Objject.
* The decision if an INSERT or UPDATE is
needed is made in the BO(Server-Side) derivation. */
public
void store() {
switch
(frmTask.frmCC.RunVersion)
{
/* Decide
what version the application runs.
*/
case JSBS_StartFrame.CONST_StandAlone:
/* Database
is running on the local machine; construct the 'Server-Side' BO
directly.
* Pass all necessary connection-structures
and this 'Client-Side' BO. */
// JS_ErrDB_Project_BOS
bosJS_ErrDB_Project_BOS
=
// new
JS_ErrDB_Project_BOS(frmTask.structMinParm,
// frmTask.frmCC.structJSBS_DB_ConnectionManager,
// this);
/* Call
the method to perform the database-operation(s).
*/
// bos_BOS.store();
/* Transfer
the values as they include the Status and
* changes
of Common Attributes (performed by the BOS)
*/
// getJS_ErrDB_Project_BO(bosJS_ErrDB_Project_BOS);
break;
case JSBS_StartFrame.CONST_FatClient:
break;
}
top.
Define
the Business Object as a variable of the Task-Frame:
That
the methods of a Business Object can be accessed, it has to be
defined as a variable and then constructed.
There are two
variables of a Business Object in a Task-Frame for the following
reason:
One is the state as the data was read from the database
or stored or copied from another BO
while the other reflects the
actual changes an user made at the entry fields of the GUI.
With
a ability to compare those two BO, buttons for 'Store' and 'Copy'
can be enabled/disabled and a warning can be displayed if the frame
should be closed without storing changed data before.
First,
the BO has to be defined as variables:
/*
* Business
Objects maintained within this task. */
protected
JS_ErrDB_Project_BOC structJS_ErrDB_Project_BOC_Read;
protected
JS_ErrDB_Project_BOC structJS_ErrDB_Project_BOC_Processed;
Then,
the BO has to be constructed.
This is done in the method that is
called before the frame is build:
private
void initialize_before_frame(String
parmstrLanguageCode) {
/*
Construct the Business Objects maintained by this task.
*/
structJS_ErrDB_Project_BOC_Read
= new
JS_ErrDB_Project_BOC(this);
structJS_ErrDB_Project_BOC_Processed
= new
JS_ErrDB_Project_BOC(this);
N.B.:
To
construct the BO in the same line as the variable is defined fails
for the following reason:
The construction of the BO refers to
the structures with the connections (either to the database-system
or to the Java Application Server) which are defined in the
Start-Frame (Command-Center).
As the reference to the Start-Frame
is available after the construction of the Task-Frame, the
references to the structures with the connections is not yet valid
at the time, when the BO is defined as variable.
top.
Implementing
the Action-Listener and the method to be triggered when a button is
clicked:
That
a reaction to a button-click can be processed, the interface
ActionListener has
to be added to the Task-Frame.
As an expansion to the Start-Frame
(see JS_FC01i – Create and code the
class for the 'Task-Frame' to maintain 'Projects'), where the
interface and the associated method is implemented in the derived
class, now the interface and the associated method is implemented in
the base class (JSBS_TaskFrame).
The
advantage of this practice is, that the set of this code is already
present in derived classes.
To be able to react to button-clicks,
it is only neccessary to add the ActionListener
and the ActionCommand
to each button and code the method actionPerformed
in the derived class.
Let
us start with the additional code in the base class
JSBS_TaskFrame.
First,
the package with the event-handler has to be imported:
package
js_base.frame;
import
java.awt.event.*;
import
javax.swing.*;
import
js_base.structures.*;
Second,
the interface has to be added:
public
class JSBS_TaskFrame
extends
JFrame implements
ActionListener {
The
previous code will lead to an error because the interface requieres
a method actionPerformed;
that will be implemented now:
/*
*
-------------------------------
* Method that is requiered
together with the interface ActionHandler.
* This
method has to be overwritten in the derived class. */
public
void actionPerformed(ActionEvent
e) {
}
Then,
the method actionPerformed
will be overwritten in the class
JS_ErrDB_Project.
So,
when any button is clicked, this method is called and code to
process the button-click can be entered.
public
void actionPerformed(ActionEvent
parmActionEvent) {
}
top.
Call
the methods of the Business Object when the button 'store' is
clicked:
That
a button calls the method actionPerformed,
the ActionListener
must be 'added' to the button.
This is done in the method that
creates the GUI-element button.
private
JButton get_btn_Store() {
/*
The code of this method auto-creates the element if it is not
already defined */
if
(btn_Store
== null) {
try
{
btn_Store
= new
JButton();
btn_Store.setName(“btn_Store“);
btn_Store.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
btn_Store.addActionListener(this);
btn_Store.setActionCommand
("btn_Store");
}
catch
(Throwable Exc) {
System.out.println(“Error
while building
btn_Store“);
Exc.printStackTrace();
}
}
return
btn_Store;
}
Furthermore,
an unique identifier (the ActionCommand)
has to be given to the button as the method actionPerformed
is called when any button (with an added
ActionListener)
is
clicked.
btn_Store.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
btn_Store.addActionListener(this);
btn_Store.setActionCommand
("btn_Store");
The
first code in the method actionPerformed
is, to find out from which button the
trigger came.
public
void actionPerformed(ActionEvent
parmActionEvent) {
String
cmd = parmActionEvent.getActionCommand();
}
If
it was from the button 'Store', then the values of the GUI-elements
are transfered to the Business Object and the method 'store' is
called.
public
void actionPerformed(ActionEvent
parmActionEvent) {
String cmd
= parmActionEvent.getActionCommand();
if
(cmd.equals("btn_Store"))
{
structJS_ErrDB_Project_BOC_Processed.getFromGUI(get_txt_ProjectCode(),
get_txt_LanguageCode(),
get_txt_TargetDirectory);
structJS_ErrDB_Project_BOC_Processed.store();
}
}
top.
Next
Steps:
